|
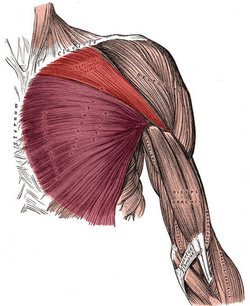
UPDATED: The pectoralis major muscle is the largest muscle in the anterior aspect of the thorax. It is thick and fan-shaped. It attaches superiorly to the medial 2/3rds of the clavicle, and medially to the anterior aspect of the sternum and cartilages of the first to sixth or seventh ribs, extending inferiorly to attach to the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. Laterally, this muscle attaches to the lateral lip of the intertubercular groove (bicipital groove) of the humerus by a two-layered quadrilateral tendon which inserts each of the two heads of the muscle.
The superficial tendon attaches the clavicular head (red in the accompanying image), which extends between the intertubercular groove of the humerus and the clavicle. The deep tendon attaches the sternocostal head (purple in the accompanying image), which extends between the humeral intertubercular groove and the attachments in the sternum, costal cartilages, and the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. There is usually a well-defined interval between the two heads of the pectoralis major.
The pectoralis major is innervated by the medial pectoral nerve (C8-T1) and lateral pectoral nerve (C5-C7).
This muscle is covered by the pectoral fascia. An extension of this fascia is the clavipectoral fascia. In both male and female, the mammary gland is situated anterior to and anchors to the pectoral fascia by a number of fascial ligaments known as "Cooper's ligaments"
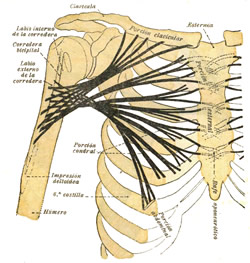
When both pectoral heads contract as a unit, the muscle adducts. flexes, and medially rotates the shoulder joint and humerus, such as when swimming doing and Australian crawl. Testut & Latarjet (1931) describe three separate muscular segments to this muscle, a clavicular component, a superior sternocostal component, and an inferior sternocostal component. They state that the clavicular components is quite evident, but the other two, although difficult to see, are separate. The clavicular head draws the humerus forward, upward, and medially, such as when you reach for something in front and above you. The sternocostal head draws the humerus down, forward, and medially.
The second image in this article is from Testut & Latarjet (1931) and shows the direction of muscular fibers of the three segments of the pectoralis major.
The word pectoral arises from the Latin term "pectum" meaning "chest, breast". In its true meaning, pectoral or pectoralis refers to a "chest plate" or an "adornment of the chest".
|
Pectoralis major muscle
Click on the image for a larger depiction
Pectoralis major. Direction of the muscular fibers
Click on the image for a larger depiction
|