|
The Holly is a tree/shrub of the genus Ilex , with perhaps the most well know being Ilex aquifolium. The plant has shiny prickly evergreen leaves and bright red berries. Cut branches of Holly are widely used as a traditionally Christmas decoration especially in wreaths and Christmas cards as illustrations. “The Holly and the Ivy” is a popular traditional English Christmas carol.
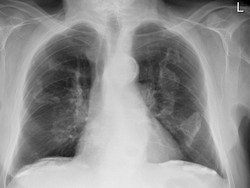
The [Holly leaf sign] refers to the appearance of calcified pleural plaques seen on chest radiographs. Pleural plaques are common in patients who have been exposed to asbestos, are asymptomatic and are most useful as a marker of asbestos exposure or asbestosis. They can be identified in 3-14% of dockyard workers and in 58% in insulation workers.
They are themselves not malignant, but patients with this plaques have a greater risk of mesothelioma and bronchogenic cancer than the general population and patients with exposed to asbestos but not pleural plaques.
|
Holly leaf sign.
Click on the image for a larger depiction
|
| The plaques arise in the parietal pleura and have predilection for the diaphragmatic dome and the undersurface of the lower posterolateral ribs. Rarely involve the visceral pleura but occasionally they are found in the fissures of the lungs.
On plain radiographic plaques appear as a geographic, usually calcified, opacities with irregular but well-defined edges. The irregular thickened nodular edges of the pleural plaques are likened to appearance of a Holly leaf, which has sharp spines along its margin.
Sources:
1. Jane R, Gulati A., Dwivedi R., Avula S., Curtis J., Abernethy L. (2013) We wish you a Merry X-Ray-mas: Christmas signs in radiology. BMJ 347:f7020 doi: 10.1136/bmj.f7020
2. Walker C., Takasugi J., Chung J., Reddy, G., Done S., Pipavath S., Schmidt R., Godwin J. (2012). Tumor-like Conditions of the Pleura. Radiographics 32:971–985.
3. Case radiograph courtesy of Dr Çağlayan Çakır, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 22986
Figure below. Ilex aquifolium. Courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 12398
Holly leaf sign.
Click on the image for a larger depiction
Article submitted by: Prof. Claudio R. Molina, MsC..
|