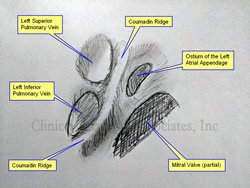
Coumadin ridge
Click on the image for a larger version
UPDATED: The [Coumadin ridge], also known as the [Warfarin ridge], or a [left atrial pseudotumor]. is an excessive elevation or protrusion of a normal ridge found between the left superior pulmonary vein and the internal ostium of the left atrial appendage. Usually this ridge will extend inferiorly towards and anterior to the ostium of the left inferior pulmonary vein. The Coumadin ridge is considered an anatomical variation of the otherwise small ridge, known as the left lateral ridge.
Because of its location and morphology, some cardiologists and radiologists have mistaken this elevation or fold of the internal anatomy of the left atrium for a thrombus and prescribed anticoagulant therapy (Coumadin or Warfarin) when none was needed, hence its name.
To understand the generation of the Coumadin ridge we must understand the embryology of this area of the heart. The left atrial appendage is the original left atrium in the embryo, which is displaced anteriorly and superolaterally when the veins that enter the atrium start to dilate at their distal end creating the left sinus venarum. After the left atrium proper has formed, the left atrial appendage is left as nothing more than an embryological remnant that can cause problems if the patient has atrial fibrillation (AFib). The ridge forms at the point where the left atrial appendage and the sinus venarum meet.
The Coumadin ridge can vary in morphology, from presenting as an elevated ridge, to a bulbous, pedunculated mass that seems to float within the left atrial appendage and undulate, following the cardiac motion, forcing the cardiologist into believing they are in the presence of a thrombus or a tumor within the heart.
This fold of tissue may contain the ligament of Marshall, autonomic nerves, and a small artery. In rare cases there may be an actual tumor arising from the location of the Coumadin ridge, but this is just a coincidence.
Now that the Coumadin ridge is a better known anatomical variation, cardiologist sometimes refer to their finding as a pseudotumor, a description that may scare the patient, but is only but a fold of tissue inside the heart.
Finding a Coumadin ridge in a patient with atrial fibrillation can be an interesting situation requiring differential diagnosis, as a patient with AFib can present with thrombi in the left atrial appendage. What to do? Is it or is it not a thrombus? Also, a differential diagnosis is needed in the case where the image is actually that of a left atrial tumor or an atrial myxoma.
The accompanying image is own work based on Sra (2004) and McKay (2008), and is a graphite on paper sketch. The image shown an internal view of the left atrium showing the left superior and inferior pulmonary vein, the ostium of the left atrial appendage and a segment of the area of the mitral valve.
We would like to thank Dr. Randall K Wolf, a contributor to Medical Terminology Daily for suggesting this article.
Sources:
1. “Coumadin ridge: An incidental finding of a left atrial pseudotumor on transthoracic echocardiography” Lohdi,AM, et al. World J Clin Cases. 2015 Sep 16; 3(9): 831–834
2. “Coumadin ridge” Tasco, V. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/coumadin-ridge
3. “Papillary fibroelastoma arising from the coumadin ridge” Malik, M, Shilo, K, Kilic,A. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2017;9(2):118-120.
4. “‘Coumadin ridge’ in the left atrium demonstrated on three dimensional transthoracic echocardiography” McKay,T., Thomas, L. Europ J Echocard (2008) 9, 298–300
5. “Endocardial imaging of the left atrium in patients with atrial fibrillation” Sra J; Krum D; Okerlund D; Thompson H. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004 Feb; Vol. 15 (2), pp. 247