|
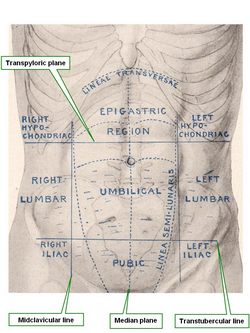
UPDATED: In surface anatomy the abdomen can be divided into nine regions by named lines (or planes): transpyloric, transtubercular, and midclavicular. These regions have specific visceral content.
• Hypochondriac regions (right and left): [Hypo]="below"; [chondr]="cartilage"; [iac]=”pertaining to”. In this context, the term means “below or deep to the cartilage (of the ribs)". The right hypochondriac region contains the liver, gallbladder, portal vein, and the right colic flexure. The left hypochondriac region contains the stomach, spleen, tail of the pancreas, and left colic flexure. For a detail on how the name of this region relates to a mental disorder, click here.
• Epigastric region: [Epi]="above"; [gastr]="stomach”; [ic]=”pertaining to". The term means “above the stomach”. This region contains mostly stomach and abdominal esophagus
• Lumbar regions (right and left): Right and left lumbar regions. The term [lumbar] refers to the area of the loins. The right lumbar region contains the ascending colon and part of the right kidney. The left lumbar region contains the descending colon and part of the left kidney
• Umbilical region: Centered around the umbilicus, this region contains mostly small intestine, abdominal aorta, and greater omentum
|