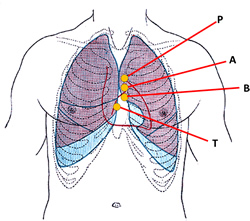
Anterior view of the thorax, showing surface
relations of bones, lungs (purple), pleura (blue),
and heart (red outline).
P. Pulmonary valve. A. Aortic valve.
B. Bicuspid valve. T. Tricuspid valve
This is a combined word arising from terms [atrium], [ventricle], and [sulcus]. For the etymology of each word, click on the corresponding link.
The atrioventricular sulcus, also know as the "coronary groove" or "coronary sulcus" is an evident incomplete groove between the atria and ventricles of the heart. It is complete posteriorly and is separated anterosuperiorly by the roots of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. It contains the right coronary artery on the right side, and the circumflex artery on the left side, hence the name "coronary groove". These coronary arteries are not visible as they are usually covered by the epicardium and subepicardial fat.
The atrioventricular sulcus (and the corresponding coronaries) are also in relation to the deeper situated atrioventricular (AV) valves, the tricuspid valve on the right; and the mitral or bicuspid valve on the left side. The accompanying image depicts the location of the AV valves, and therefore the location of the AV sulcus. The image is an anterior view of the thorax, showing surface relations of bones, lungs (purple), pleura (blue), and heart (red outline). P. Pulmonary valve. A. Aortic valve. B. Bicuspid valve. T. Tricuspid valve
Sources:
1. "The Origin of Medical Terms" Skinner, HA 1970 Hafner Publishing Co.
2. "Medical Meanings - A Glossary of Word Origins" Haubrich, WD. ACP Philadelphia
3 "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8 Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
4. "Anatomy of the Human Body" Henry Gray 1918. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger
Image modified by CAA, Inc. Original image by Henry Vandyke Carter, MD., courtesy of bartleby.com