|
The lumbar region of the spine is composed by five lumbar vertebrae. Although sharing characteristics common to all vertebrae, a lumbar vertebra can be differentiated by the following:
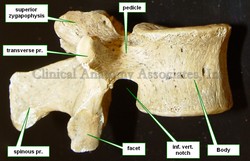
• The vertebral body is large, tall, and when viewed from superior, the vertebral body has a longer transverse diameter and a shorter anteroposterior diameter. Most anatomists describe the vertebral body as being “kidney-shaped”. The massiveness of the vertebral body is due to the larger weight that each consecutive vertebra has to bear in the lumbar region. Because of this, lumbar vertebrae have larger anular epiphyses, and the vertebral body is hourglass-shaped with a “waist”. As with other vertebrae, the body of a lumbar vertebra has vertebral endplates, nutritional foramina, and in its posterior aspect they present with basivertebral foramina.
• The pedicles in the lumbar vertebrae are larger, course in a mostly anteroposterior direction, and have a oval cross-section where the superoinferior diameter is longer and the transverse diameter is shorter. This is important for transpedicular procedures for vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.
• The transverse processes are also larger than other vertebrae. Of interest are the facts that the transverse process of the third lumbar vertebra is the longest of all lumbar vertebrae and that the transverse process of the fifth lumbar vertebra courses superolaterally at an angle of almost 45 degrees because of the presence of the strong iliolumbar ligament. The lumbar transverse processes have a small tubercle called the mammillary process.
• The lumbar spinous processes are large and have a square shape.
Again, because of the larger weight bearing capacity of the lumbar vertebrae, they have strong ligaments and their zygapophyseal joints and articular facets tend to be oriented with their surfaces in a transverse plane. This has two consequences: The rotational mobility of the whole lumbovertebral region is limited and they tend not to have anteroposterior displacement.
|
Lumbar vertebra - Lateral view.
Lumbar vertebra - Inferior view.
|